Hi, this is Lizzy from Dinosaw ( Not a Robot ). Which Machine ( model ) do you want? Please WhatsApp us now
Get a deep dive into the core technology of gantry stone cutting machines. This article explains how its heavy steel frame, hydraulic system, and PLC automation ensure high precision.
TL;DR:Core Technology at a Glance
- Robust Structural Design:The machine’s heavy-duty steel frame and gantry structure are engineered to minimize vibration, which is the key to achieving precise, fracture-free cuts.
- PLC-Driven Automation:The PLC system acts as the machine’s brain, automating the programming of cutting dimensions, speeds, and slab thickness for unmatched consistency and repeatability.
- Stability from Hydraulic Lifting:The hydraulic system provides smooth, steady vertical movement, absorbing shocks and ensuring the blade remains stable throughout the cut—critical for brittle materials like marble.
- Next Step:Understanding how these core components work together will help you evaluate if this machine meets your technical requirements for precision and efficiency.
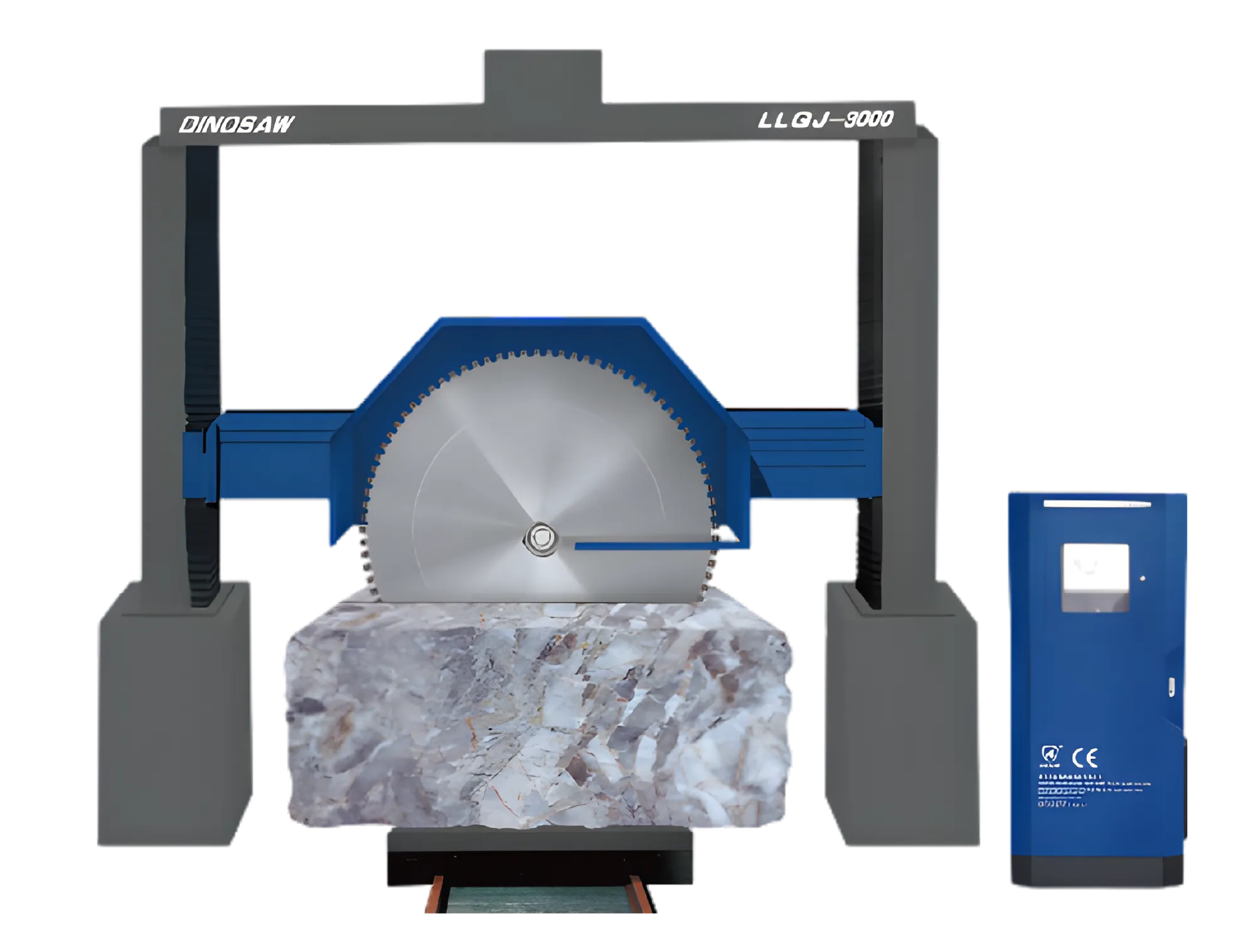
Technical Definition: What Makes Up a Gantry Block Cutting Saw?
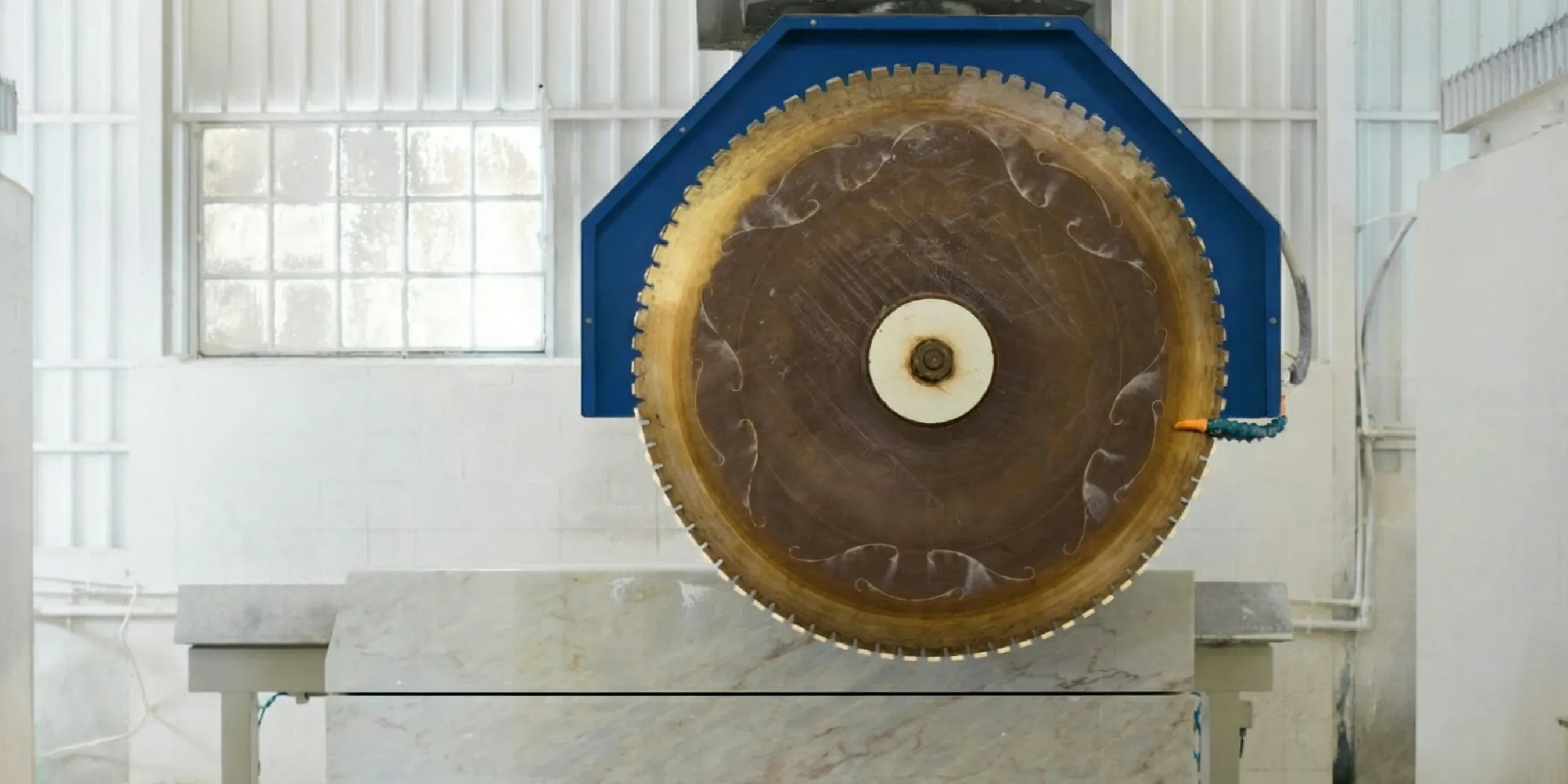
- Robust Gantry Steel Structure:This is the machine's skeleton, typically consisting of a heavy-duty steel frame that spans two parallel rails. Its primary function is to provide an extremely stable and rigid platform that resists the immense forces and vibrations generated during cutting. This stability is fundamental to achieving high-precision cuts.
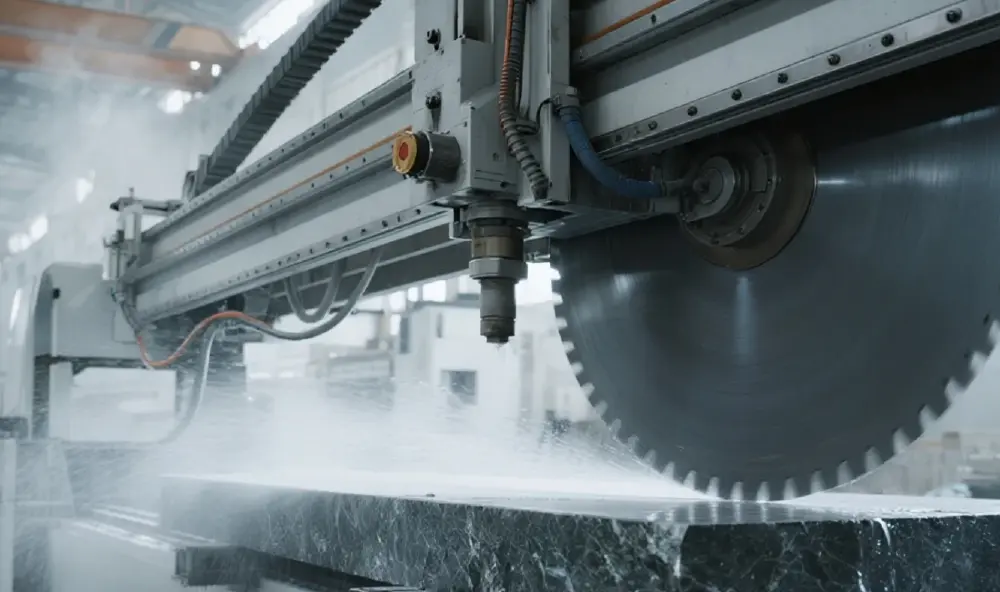
- Crossbeam and Cutting Assembly:Mounted on the gantry, the crossbeam carries the cutting tools (one or more diamond circular saw blades). This assembly moves horizontally along the gantry rails (X-axis), while the blades move transversely along the crossbeam (Y-axis), allowing coverage over the entire surface of the stone block.
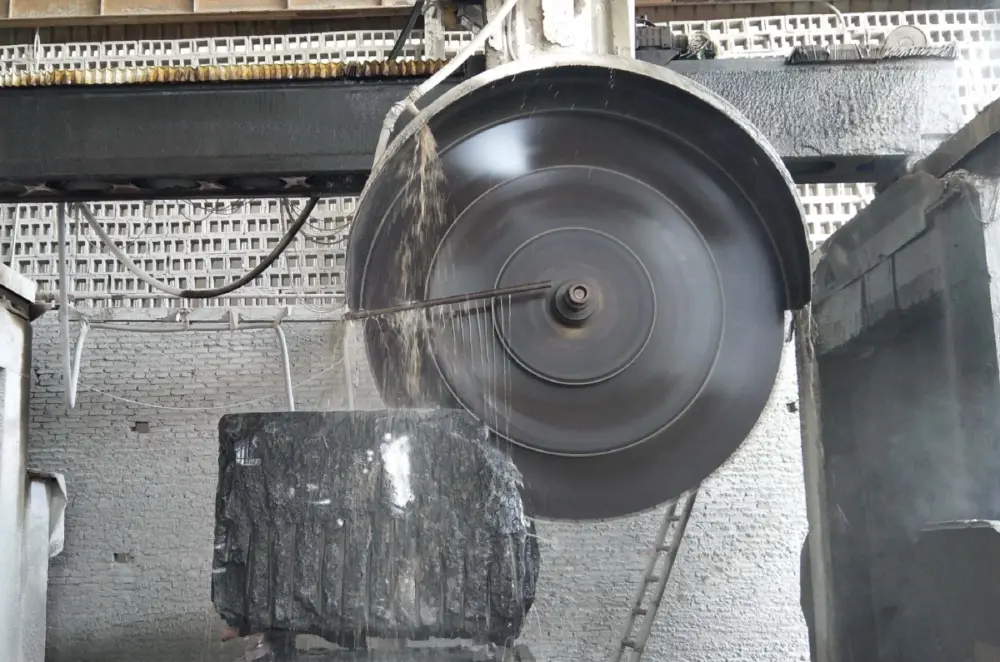
- Hydraulic Lifting System:This system controls the vertical movement (Z-axis) of the cutting assembly, responsible for setting the cutting depth with precision. Compared to mechanical screw systems, a hydraulic system offers smoother, stepless motion and effectively dampens vibrations, which is crucial for preventing micro-fractures in hard, brittle materials.
- PLC Automation Control:The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is the "brain" of the machine.According to Wikipedia, a PLC is an "industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes."Operators use an interface to input parameters like desired slab thickness, number of cuts, and speed, and the PLC then automates the entire cutting sequence, ensuring consistency and repeatability every time.
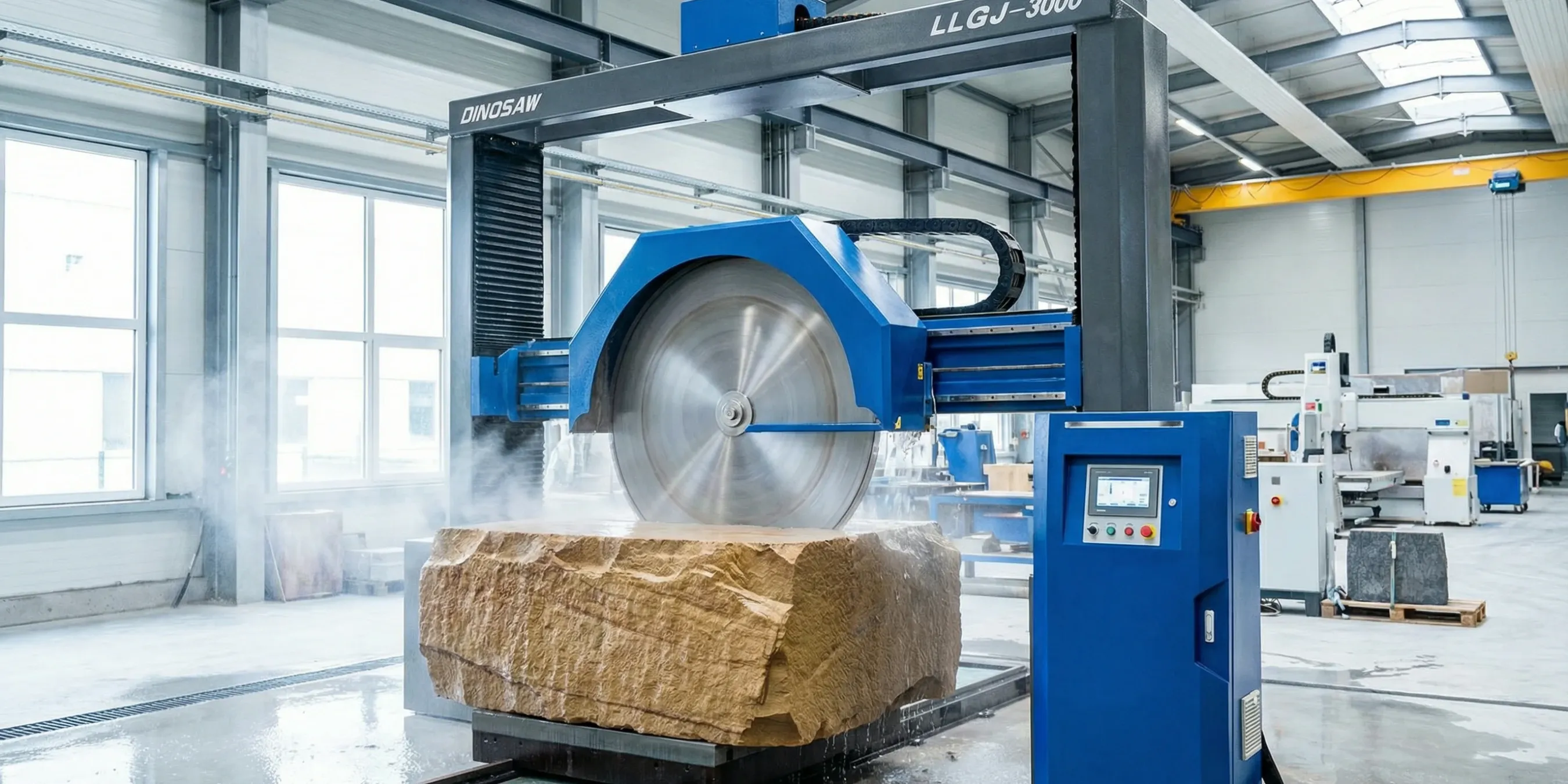

Principles & System Architecture for the PLC-Controlled Gantry Saw
Motion Axes and Feed Directions
- X-Axis:Longitudinal movement of the gantry along the rails on the factory floor.
- Y-Axis:Transverse movement of the cutting head assembly along the crossbeam.
- Z-Axis:Vertical up-and-down movement of the blade via the hydraulic system.
Control and Cooling Systems
- Closed-Loop Control:Encoders monitor blade position and speed, feeding data back to the PLC, which continuously adjusts motor and hydraulic outputs to match presets.
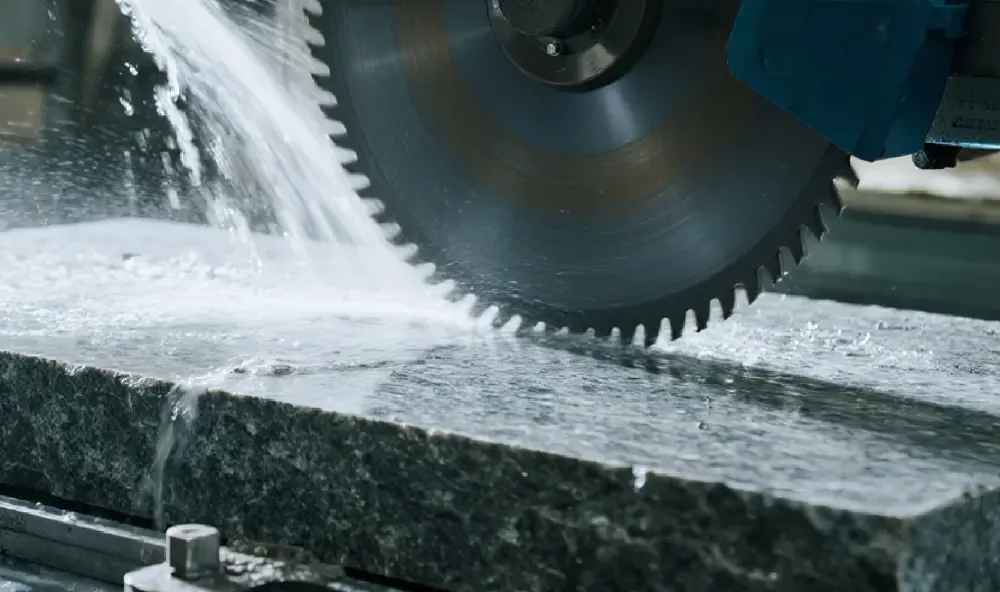
- Water Cooling System:A critical subsystem that sprays water directly at the cutting point to cool the blade and suppress dust. This not only prevents blade overheating and warping but is also a key measure for complying with safety regulations on respirable crystalline silica from bodies like OSHA.
Core Technical Advantages of the Heavy-Duty Gantry Cutter
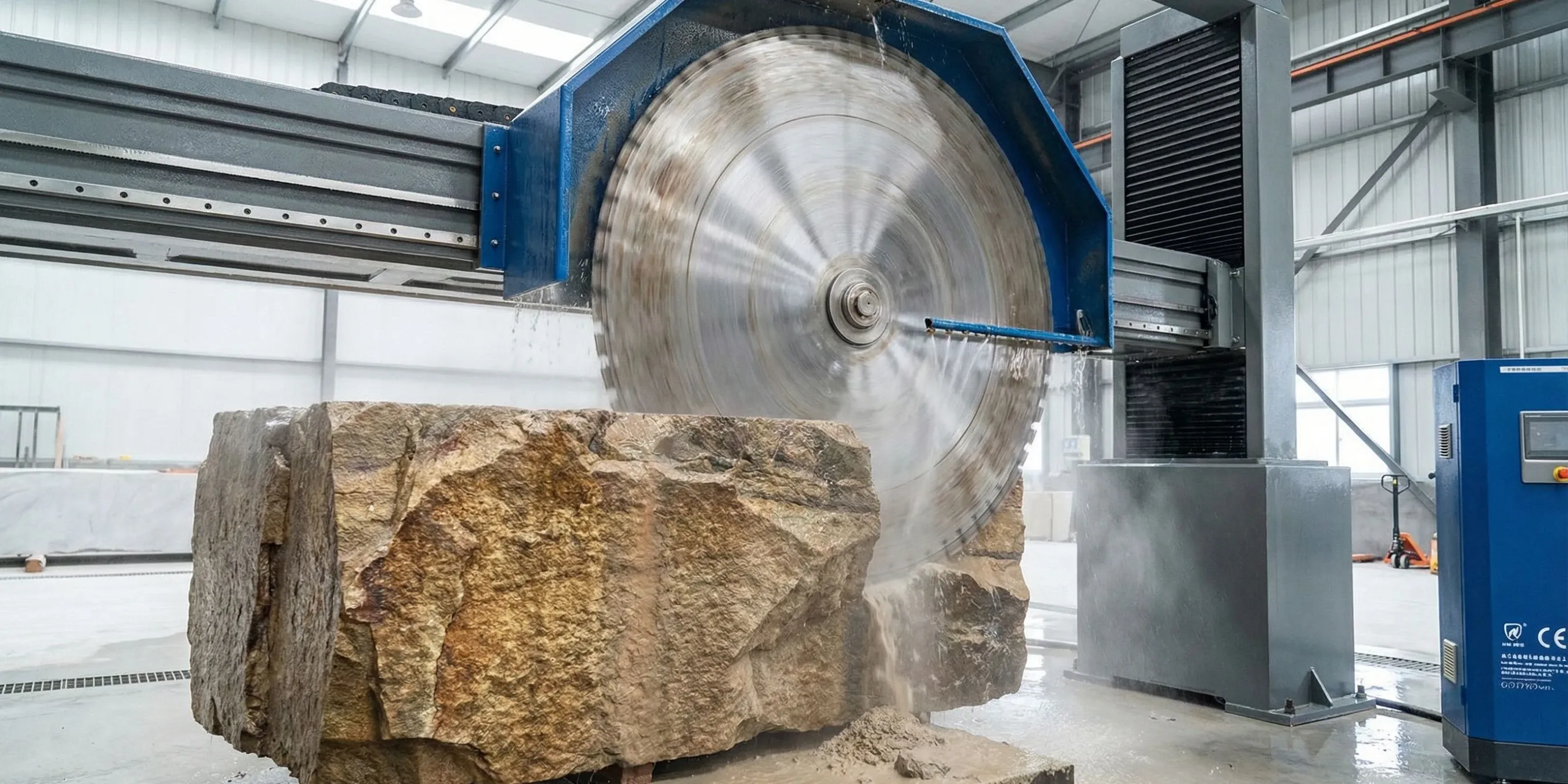

Key Components and Ranges of the Gantry Block Cutting Saw
Component | Technical Specification Range | Engineering Significance |
|---|---|---|
Diamond Blade | Diameter: 2200 mm to 3000 mm | Determines the maximum cutting depth. A larger diameter can handle thicker blocks. |
Main Motor | Power: 30 kW to 37 kW | Provides the torque needed to drive the blade. Higher power is more effective for cutting hard stones like granite. |
Frequency Converter | Enables stepless adjustment of blade linear speed and feed rate. | Allows operators to optimize cutting parameters based on stone hardness and density, improving cut quality and tool life. |
Worktable | Dimensions: Typically 2000 mm x 2000 mm | Defines the maximum footprint of a stone block that can be placed on it for processing. |
Water Cooling System | Water Consumption: Approx. 10 m³/h | Must provide sufficient flow to cool the blade effectively and suppress dust. Inadequate flow leads to premature blade failure. |
Guide Rail System | Consists of high-precision machined steel rails. | Ensures smooth, linear movement of the gantry and cutting assembly. The accuracy of the rails directly impacts the flatness of the final slab. |
Hydraulic Station | Provides stable pressure for the lifting system. | The reliability of the hydraulic system is crucial for maintaining consistent cutting depth and absorbing vibrations. |
Common Failures & Mitigation for the Gantry Stone Cutter
- Blade Overheating:Typically caused by insufficient water cooling or an excessive feed rate.
- Mitigation:Immediately check for clogged nozzles and ensure water flow is at the recommended 10 m³/h. Also, reduce the feed rate using the frequency converter, especially when cutting hard granite.
- Cutting Misalignment:Can be caused by worn guide rails, improper blade tension, or a misaligned frame.
- Mitigation:Regularly inspect the guide rails for straightness and clear any debris. Verify that the blade is correctly installed and tensioned. If the issue persists, perform a full frame alignment procedure.
- Hydraulic Leakage:Often a result of worn or damaged seals.
- Mitigation:Implement a preventive maintenance schedule to replace hydraulic hoses and seals at regular intervals. Visually inspect for any signs of leakage at the start of each shift.
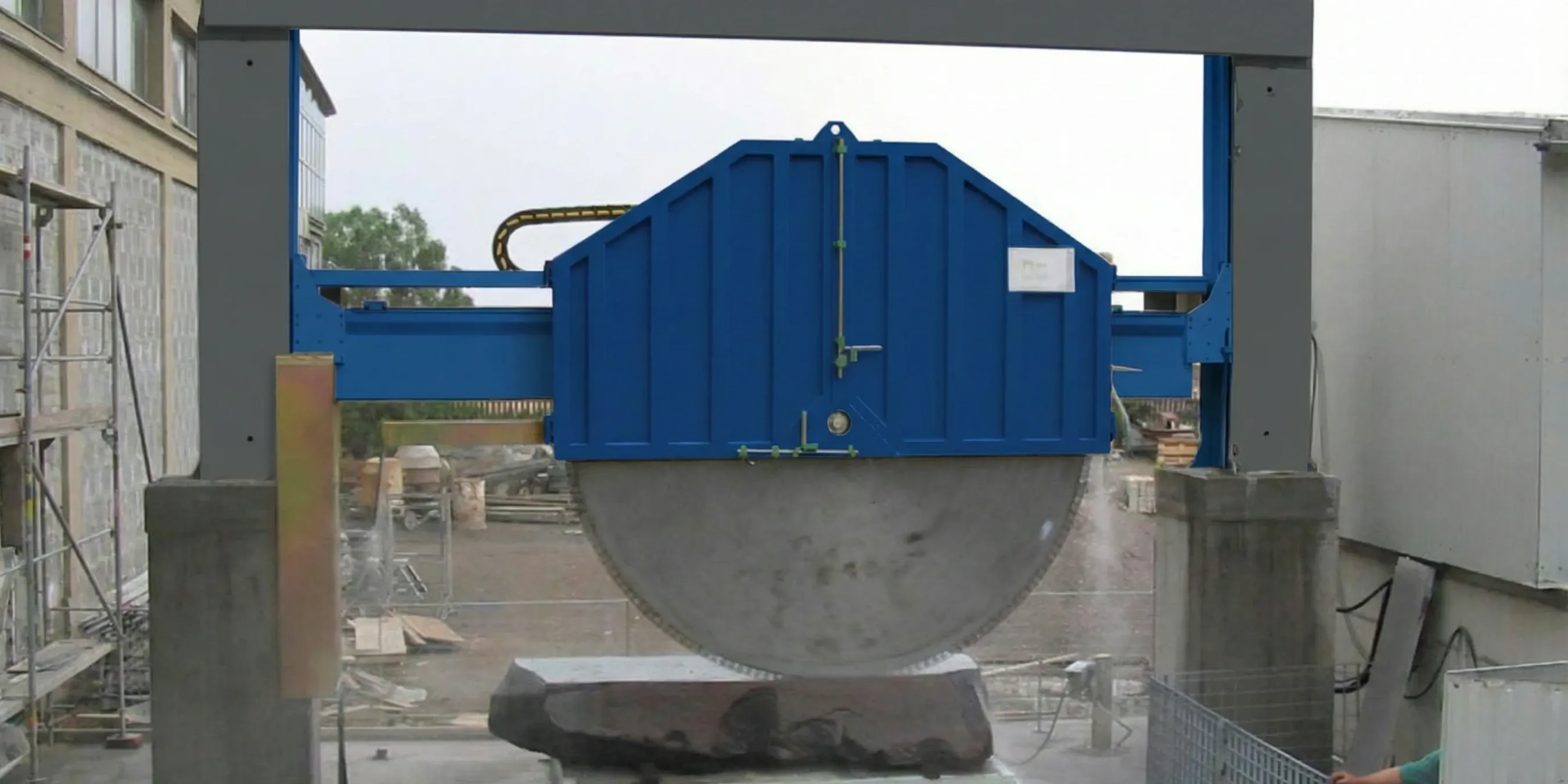

System Compatibility and Integration for Industrial Stone Gantry Cutter
Starting Parameter Settings for the Gantry Slab Cutter
- Hard Granite:Start with a slower feed and higher water flow; gradually increase feed until the cut is smooth with no chatter or edge chipping.
- Marble:Use a moderate feed with smooth hydraulic motion; prioritize stability to protect veining; adjust until the surface shows uniform texture.
- Limestone:Use a faster feed to maximize efficiency; tune down if the blade shows drag or slurry thickens.
Summary: Engineered for Performance and Reliability

Technical FAQ
How does the PLC system improve cutting accuracy?
- Context:The PLC receives feedback from encoders on the machine's axes, creating a closed-loop system. If it detects any deviation from the set path or speed, it instantly adjusts the motor or hydraulic outputs to correct the error.
- Risk:Without a PLC, operators must manually control the cutting depth and feed rate, which is prone to human error and can result in slabs of varying thickness, increasing waste.
- Next Step:When evaluating machines, consider the sophistication of the PLC interface. A user-friendly system makes it easier for operators to program complex jobs accurately, further enhancing precision.
What's the difference between hydraulic and mechanical lifting?
- Context:Hydraulic systems use fluid pressure to lift the cutting assembly, which naturally absorbs shocks and vibrations. Mechanical systems, often using a lead screw, can transmit more vibrations to the cutting head.
- Risk:Vibrations from a mechanical system can cause micro-fractures in materials like marble and granite, leading to a lower quality finish and potential slab failure.
- Next Step:For any application involving high-value, brittle stone, prioritize a machine with a hydraulic lifting system. It is a key technical feature for ensuring the structural integrity of the final product.
How important is the heavy-duty steel frame of a gantry block cutter?
- Context:Harder stones like granite require a slower, more deliberate feed rate to prevent excessive blade wear, while softer stones like limestone can be cut much faster. The frequency converter enables this adjustment on the fly.
- Risk:Without a frequency converter, the machine would run at a fixed speed, which is inefficient and leads to either poor cut quality on hard materials or unnecessarily slow production on soft materials.
- Next Step:During operator training, create a settings chart that maps optimal feed rates to the different types of stone you process. This becomes a valuable reference for your team.
How important is the Gantry Stone Block Cutting Machine heavy steel frame?
- Context:Cutting through a large stone block generates immense forces and vibrations. A lighter frame would flex and vibrate, causing the blade to deflect and resulting in an uneven, inaccurate cut. The heavy frame provides the mass and rigidity to absorb these forces.
- Risk:A machine with an inadequate frame will suffer from constant vibration, leading to faster wear on all components, poor cut quality, and a shorter operational lifespan.
- Next Step:When comparing machines, look at the total weight and the thickness of the steel used in the gantry and crossbeam. A heavier, more robust frame is a direct indicator of higher potential precision and durability.
Why is the water cooling system critical for safety?
- Context:Cutting stone, especially granite and sandstone, releases fine particles of respirable crystalline silica. According to guidance from the CDC/NIOSH, inhaling this dust can cause serious lung diseases. Wet cutting methods suppress this dust at the source.
- Risk:Operating the machine with an inadequate or malfunctioning water system exposes operators to dangerous levels of silica dust and violates safety regulations like those from OSHA.
- Next Step:Integrate a daily check of the water cooling system into your pre-operation safety checklist. Ensure all nozzles are clear and that water flow meets the manufacturer's specification.
Can this industrial gantry cutter be integrated into an automated production line?
- Context:Through industrial communication protocols (e.g., OPC UA, Profinet, if applicable), the gantry cutter's PLC can send/receive signals to/from other machines. For example, it can signal a robotic arm or conveyor belt once a block is fully processed.
- Risk:Poor integration can create bottlenecks. If the handshake signals between machines are not configured correctly, it can lead to idle time and reduced overall factory throughput.
- Next Step:When planning your factory layout, discuss your integration needs with our engineering team. We can provide guidance on the necessary interfaces for connecting the gantry cutter to equipment like a polishing line or engraving machine .
Do I need different electrical infrastructure for different motor powers?
- Context:The electrical infrastructure, including wiring, circuit breakers, and transformers, must be rated to handle the motor's full load amperage without overheating or causing voltage drops.
- Risk:An undersized electrical service can lead to frequent circuit trips, motor damage due to low voltage, and poses a significant fire hazard.
- Next Step:Before installation, provide your licensed electrician with the machine's technical specifications. They must verify that your facility's electrical service meets or exceeds the power requirements for the specific model you choose.







 English
English 中文
中文 Italian
Italian Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch العربية
العربية Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Français
Français Русский
Русский




